Structure of the Powder Metallurgy Industry
 Powder Metallurgy IndustryThe three segments that make up the powder metallurgy industry are an unbroken chain extending from raw materials to finished components, with each link supporting, and in turn being supported by, the other links.
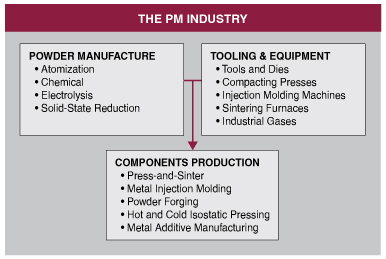
Powder Metallurgy IndustryThe three segments that make up the powder metallurgy industry are an unbroken chain extending from raw materials to finished components, with each link supporting, and in turn being supported by, the other links.
1. Producers of powders and other raw materials
These are the companies that, using a variety of techniques, including solid- state reduction, chemical, atomization, and electrolysis, manufacture the powders that are the building blocks of the PM technology. The most common metal powders available are iron and steel, tin, nickel, copper, aluminum, and titanium, as well as refractory materials such as tungsten, molybdenum, and tantalum. Companies that make lubricants and other additives that are essential to the PM process, and those that manufacture industrial gases that are used as atmospheres in sintering furnaces, are included within this segment of the industry.
2. Makers of process equipment and tooling
This industry segment consists of companies engaged in the manufacture of equipment and technology for the compaction and sintering of powder metallurgy components, including presses, injection molding machines, dies, and furnaces. It also includes suppliers of specialized equipment, systems, and support services for powder handling, secondary manufacturing and finishing operations, control automation, robotics, and laboratory testing.
3. Component and product producers
This segment embraces those firms that fabricate finished components using one of the forming technologies available. Most such companies produce these components while serving as contractors for original equipment manufactureres (OEM) who use them in their finished products, although there are a few that are in-house suppliers to such OEMs.